How Lymphedema Affects Wound Healing and Ways to Manage It
Related Questions Asked and Answered
1. What are the early signs of lymphedema that can affect wound healing?
Lymphedema often develops gradually, and recognizing early signs can help prevent complications. Key symptoms include:
- Swelling in the limbs or affected area
- A feeling of heaviness or tightness in the skin
- Reduced flexibility or mobility
- Recurring infections
- Hardening or thickening of the skin
If you notice any of these symptoms, consult a wound care specialist promptly to prevent further complications.
2. Can untreated lymphedema lead to chronic wounds?
Yes. When lymphedema is left unmanaged, excess fluid buildup can lead to skin breakdown, increasing the risk of chronic wounds such as venous ulcers and pressure injuries. Regular treatment and proper skincare can help prevent these complications.
3. How do wound care specialists treat wounds complicated by lymphedema?
At OWC Center, we provide a multi-disciplinary approach to managing wounds caused by lymphedema. Treatments may include:
- Compression therapy to reduce swelling
- Debridement to remove dead tissue and promote healing
- Infection control strategies, such as antimicrobial dressings
- Nutrition counseling to enhance the body’s ability to heal
4. Are there lifestyle changes that can improve lymphedema and wound healing?
Absolutely! Implementing the following lifestyle changes can significantly improve wound healing:
- Stay Active: Gentle movements help keep lymphatic fluid flowing.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in proteins, vitamins, and antioxidants supports tissue repair.
- Hydrate Well: Proper hydration prevents tissue dehydration and reduces swelling.
- Wear Compression Garments: Use doctor-recommended compression wear to manage fluid retention.
5. When should I seek professional help for wounds related to lymphedema?
You should seek professional help if:
- Your wound does not show signs of healing within two weeks.
- There is increased redness, swelling, or pus, indicating infection.
- The wound becomes painful or has a foul odor.
- You experience persistent or worsening swelling despite home care.
Early intervention by a wound care specialist can prevent severe complications and improve healing outcomes.
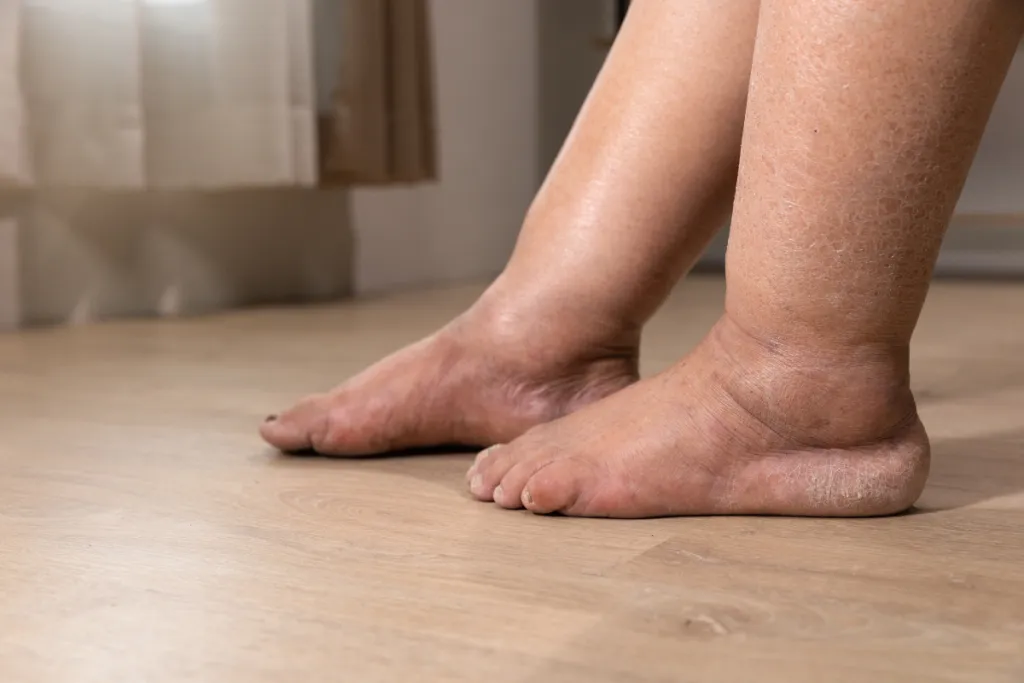
Lymphedema. A condition where excess lymph fluid accumulates in tissues, causing swelling—often in the arms or legs. Imagine waking up one day to find your leg inexplicably heavier, your skin tighter, and your mobility compromised. For many, this isn’t a distant nightmare but a daily reality.
Take, for instance, the story of a beauty queen who was once dubbed ‘elephant girl‘ after one leg doubled in size and leaked fluid. Her journey from that challenging period to a triumphant transformation is both inspiring and enlightening.
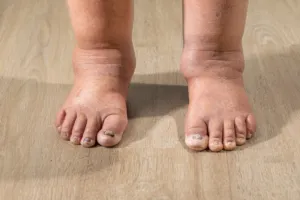
But what exactly is lymphedema? At its core, it’s a malfunction of the lymphatic system, leading to fluid retention and swelling. This isn’t just a cosmetic concern; the accumulation of lymph fluid can impede wound healing, making even minor cuts or bruises potential health risks.
Understanding the profound impact of lymphedema on wound healing is crucial. The stagnant fluid becomes a breeding ground for infections, and the swollen tissue receives less oxygen and nutrients, both of which are vital for recovery. This means that individuals with lymphedema often face prolonged healing times and a higher risk of complications.
But there’s hope. Advancements in medical treatments and a deeper understanding of lymphedema have paved the way for effective management strategies. From specialized therapies to lifestyle modifications, individuals can take proactive steps to mitigate the effects of lymphedema on wound healing.
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into the intricacies of lymphedema, its impact on wound healing, and the myriad ways to manage and overcome its challenges. Whether you’re personally affected or seeking knowledge to support a loved one, this comprehensive guide aims to shed light on this often-overlooked condition and offer actionable insights.
Understanding Wound Healing
Wound healing is a remarkable and intricate biological process that our bodies undertake to repair damaged tissue. It involves a carefully orchestrated sequence of cellular and molecular events aimed at restoring skin integrity and function. Understanding the healing process can help individuals take proactive measures to promote faster and more effective recovery from wounds.
The Stages of Wound Healing
The wound healing process occurs in four overlapping but distinct stages: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and maturation (remodeling). Each phase is essential for ensuring the wound heals correctly and minimizes the risk of complications.
1. Hemostasis: Stopping the Bleeding
The first response to a wound is hemostasis, which occurs immediately after an injury. This phase is crucial to prevent excessive blood loss and to create a stable environment for the healing process.
- Blood Clot Formation: Platelets rush to the injury site and adhere to the exposed blood vessels, forming a temporary clot.
- Fibrin Mesh Development: A protein called fibrin strengthens the clot, creating a mesh that stabilizes the wound and serves as a framework for cellular activity.
- Vasoconstriction: Blood vessels constrict to reduce bleeding, allowing the clotting mechanism to take full effect.
2. Inflammation: The Body’s Defense Mechanism
Once bleeding is controlled, the immune system initiates the inflammatory phase. This stage is often characterized by redness, warmth, swelling, and pain.
- White Blood Cell Activation: Neutrophils, a type of white blood cell, arrive at the wound site to engulf bacteria, dead cells, and debris.
- Release of Growth Factors: Macrophages replace neutrophils to continue the cleanup and release cytokines and growth factors that promote tissue repair.
- Increased Blood Flow: The blood vessels widen (vasodilation) to bring in oxygen and essential nutrients needed for healing.
3. Proliferation: Tissue Formation and Repair
During this phase, the body begins to rebuild the damaged tissue by forming new cells and blood vessels.
- Fibroblast Activity: Fibroblasts are activated to produce collagen, which provides strength and structure to the new tissue.
- Angiogenesis: New blood vessels form to supply oxygen and nutrients to the regenerating cells.
- Granulation Tissue Formation: Pink, bumpy granulation tissue develops, covering the wound base and filling the injured area.
- Re-epithelialization: Skin cells (keratinocytes) migrate across the wound to close the surface.
4. Maturation (Remodeling): Strengthening the New Tissue
The final stage of wound healing focuses on refining and strengthening the newly formed tissue. This process can last from several weeks to months, depending on the wound’s severity.
- Collagen Remodeling: Type III collagen is replaced by stronger Type I collagen, increasing tissue tensile strength.
- Scar Formation: The wound contracts, and excess fibroblast activity diminishes, resulting in scar tissue.
- Capillary Reduction: Newly formed blood vessels regress once the tissue has stabilized.
Factors Affecting Wound Healing
Several factors influence how quickly and effectively a wound heals:
- Age: Older adults may experience slower healing due to reduced collagen production and weakened immune responses.
- Chronic Conditions: Diabetes, vascular disease, and immune disorders can delay healing.
- Nutrition: Adequate protein, vitamins (A, C, E), and minerals like zinc promote tissue repair.
- Oxygenation and Blood Flow: Proper circulation is essential to deliver nutrients and oxygen to the wound site.
- Infection: Bacterial infections can disrupt healing and lead to complications.
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as steroids and chemotherapy agents, can impair the healing process.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption negatively impact wound recovery.
How to Support Wound Healing at Home
While some wounds require professional medical attention, there are steps you can take at home to promote faster healing:
- Keep the Wound Clean: Wash with mild soap and water, and apply an appropriate antiseptic to prevent infection.
- Apply Dressings: Use sterile bandages to protect the wound and maintain a moist healing environment.
- Monitor for Infection: Look for signs of infection such as increased redness, swelling, pus, or fever.
- Maintain Proper Nutrition: Eat a balanced diet rich in protein and vitamins to support tissue repair.
- Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: These substances can impair circulation and delay healing.
- Follow Medical Advice: If prescribed antibiotics or wound care treatments, follow the instructions carefully.
When to Seek Professional Wound Care
Some wounds require specialized medical attention, particularly those that are:
- Deep or Large: Wounds that expose muscle, bone, or tendons.
- Infected: Showing signs of pus, warmth, and spreading redness.
- Chronic or Non-Healing: Wounds that persist for more than 4 weeks.
- Related to Medical Conditions: Diabetic foot ulcers, pressure sores, or vascular wounds.
At Optimum Wound Care Center, our team of specialists provides expert care for all types of wounds, ensuring optimal healing outcomes.
Factors Influencing Wound Healing
Several elements can affect how efficiently a wound heals:
- Age: Older individuals may experience slower healing.
- Nutrition: Adequate nutrients are vital for tissue repair.
- Infection: Presence of bacteria can delay healing.
- Chronic Conditions: Diseases like diabetes can impede the healing process.
Lymphedema and Its Impact on Wound Healing
Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid in the tissues, leading to swelling, particularly in the arms or legs. This condition not only affects mobility and quality of life but also significantly impacts wound healing. Understanding the relationship between lymphedema and wound healing is crucial for patients and caregivers to take proactive measures in managing symptoms and preventing complications.
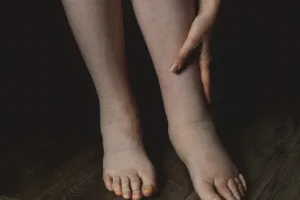
How Lymphedema Impairs Wound Healing
Lymphedema creates several challenges for wound healing due to fluid buildup, compromised circulation, and increased infection risks. Below are the key ways in which lymphedema impairs the body’s natural healing process:
1. Fluid Accumulation and Skin Vulnerability
Excess lymphatic fluid causes swelling and stretches the skin, making it more prone to injuries. The skin may become fragile, dry, and prone to cracks or ulcers, which can quickly develop into chronic wounds if not properly managed.
2. Reduced Oxygenation of Tissues
Swollen tissues in lymphedema patients often suffer from reduced oxygen supply. Oxygen is a vital component for cellular repair and regeneration, and its deficiency can delay wound closure, increasing the risk of non-healing wounds.
3. Increased Risk of Infection
Lymphatic fluid that stagnates in tissues creates an ideal environment for bacterial growth. Lymphedema patients are more susceptible to infections such as cellulitis and chronic wounds that do not heal properly. Once an infection sets in, it can quickly spread, leading to severe complications.
4. Impaired Immune Response
The lymphatic system plays a critical role in immune function. When lymphedema disrupts lymph flow, it weakens the immune response, making it harder for the body to fight off infections and repair damaged tissues.
5. Delayed Removal of Waste Products
Healthy circulation is essential for clearing metabolic waste and toxins from tissues. In lymphedema patients, sluggish lymphatic drainage hinders this process, leading to prolonged inflammation and slow wound healing.
Strategies to Improve Wound Healing in Lymphedema Patients
While lymphedema poses challenges to healing, several strategies can help manage symptoms and promote better wound outcomes:
1. Compression Therapy
Compression bandages or garments help reduce fluid buildup, improve circulation, and prevent further swelling. These should be used under the guidance of a wound care specialist.
2. Proper Wound Care
- Keep wounds clean and dry to prevent infections.
- Use appropriate dressings that support healing and manage excess moisture.
- Seek professional wound care services for debridement or advanced treatment when needed.
3. Lymphedema Management Techniques
- Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) performed by a trained therapist can encourage proper lymph fluid movement.
- Elevating the affected limb helps reduce swelling and improves circulation.
- Regular physical activity tailored to individual needs supports fluid movement.
4. Skin Care and Protection
- Moisturize daily to prevent dryness and cracking.
- Avoid cuts, scrapes, and insect bites that can lead to infections.
- Wear protective clothing and proper footwear to minimize injury risks.
5. Nutrition and Hydration
- A balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins C and E, and zinc can enhance wound healing.
- Staying hydrated supports overall lymphatic function and tissue repair.
6. Medical Interventions
For severe cases, medical treatments such as pneumatic compression devices, laser therapy, or surgical interventions may be necessary to manage lymphedema and support wound healing.
When to Seek Professional Wound Care
If you have lymphedema and develop a wound that is slow to heal, painful, or showing signs of infection (redness, swelling, warmth, pus, or fever), it’s crucial to seek professional wound care immediately. Early intervention can prevent complications and promote faster healing.
At OWC Center, we specialize in advanced wound care treatments tailored to patients with conditions like lymphedema. Our expert team offers personalized care plans, including compression therapy, wound debridement, and infection management, to support optimal healing.
Recognizing Early Signs of Lymphedema
Early detection is key to managing lymphedema effectively:
- Swelling: Especially in limbs.
- Heaviness or Tightness: A feeling of fullness in the affected area.
- Restricted Movement: Difficulty moving joints.
- Recurring Infections: Such as cellulitis.
- Skin Changes: Hardening or thickening.
Management Strategies for Lymphedema
Effectively managing lymphedema involves a combination of therapies and lifestyle modifications:
- Compression Therapy
Using garments or bandages to apply pressure helps reduce swelling and aids lymph fluid movement.
- Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD)
A specialized massage technique that stimulates lymph flow.
- Exercise
Engaging in gentle activities promotes lymphatic circulation.
- Skin Care
Keeping the skin clean and moisturized prevents infections.
- Pneumatic Compression Devices
These devices use air pumps to apply pressure, facilitating lymph movement.
- Surgical Options
In severe cases, procedures like lymph node transfers might be considered.
Lifestyle Modifications
Incorporating certain habits can significantly improve quality of life:
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet supports overall health.
- Hydration: Drinking adequate water aids bodily functions.
- Avoiding Tight Clothing: Prevents constriction of lymph flow.
- Protecting the Affected Limb: Minimizes injury risk.
The Role of Wound Care Specialists
Consulting professionals ensures tailored treatment plans:
Comprehensive Assessment: Understanding Lymphedema is more than just swelling—it’s a serious condition that can have profound effects on wound healing. When excess lymph fluid accumulates in tissues, it creates an environment where wounds struggle to close, infections become more likely, and healing is significantly delayed. The skin, stretched and vulnerable, is at greater risk for injuries that take much longer to mend.
However, effective management can make a world of difference. Early detection of symptoms—such as swelling, tightness, and recurring infections—allows for proactive treatment that reduces complications. Compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage, and specialized wound care interventions help control fluid buildup and support healing. Lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet, staying active, and maintaining proper hydration, further improve outcomes.
By addressing lymphedema with a comprehensive approach, individuals can not only enhance their wound healing process but also improve their overall quality of life. Consulting a wound care specialist ensures access to tailored treatments that prevent complications and promote recovery. With the right care, living well with lymphedema is entirely possible.
Key Takeaways
- Early Detection of Lymphedema Can Prevent Complications
Recognizing the first signs of lymphedema—such as swelling, tightness, and recurring infections—can help prevent severe complications. Early intervention with specialized wound care can reduce swelling and improve healing outcomes before chronic wounds develop. - Lymphedema Increases the Risk of Chronic Wounds
Excess lymph fluid creates an environment where wounds struggle to heal, increasing the risk of infections and complications. Proper management through advanced wound care techniques can minimize this risk and promote faster recovery. - Compression Therapy Supports Wound Healing
Wearing doctor-recommended compression garments can help control swelling, improve circulation, and enhance wound healing. A wound care specialist can provide tailored compression solutions for effective lymphedema management. - Lifestyle Changes Can Improve Lymphedema and Healing
Staying active, eating a nutritious diet, and keeping the skin moisturized are essential for managing lymphedema. A holistic approach that includes personalized wound care plans ensures better long-term health. - Professional Wound Care is Essential for Managing Lymphedema
If you have lymphedema-related wounds, seeking help from a wound care expert can prevent complications and promote healing. Specialized treatments like debridement, antimicrobial dressings, and lymphatic drainage can make a significant difference in recovery.

