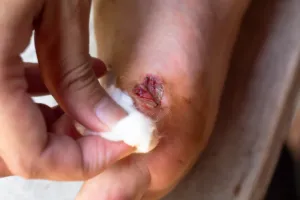
Diabetic Foot Care Tips to Prevent Ulcers and Infections
Common Questions About Diabetic Foot Care
1. Why are people with diabetes at higher risk for foot ulcers?
Diabetes affects circulation and nerve function, leading to:
- Reduced sensation in the feet (neuropathy), making it harder to feel injuries.
- Poor blood flow (peripheral artery disease), delaying healing.
- Higher risk of infection due to a weakened immune system.
Without proper care, minor cuts or blisters can turn into serious ulcers. Regular foot checks and early intervention are crucial to preventing complications.
2. How can I prevent diabetic foot ulcers?
To minimize ulcer risks:
- Keep your feet clean and dry.
- Avoid tight or poorly fitted shoes.
- Inspect your feet daily for wounds or signs of irritation.
- Maintain good blood sugar control.
- Schedule regular foot exams with a specialist.
Early detection and proper wound care can prevent minor issues from escalating. Explore our advanced wound care services.
3. What should I do if I notice a wound on my foot?
If you discover a wound:
- Clean it gently with mild soap and water.
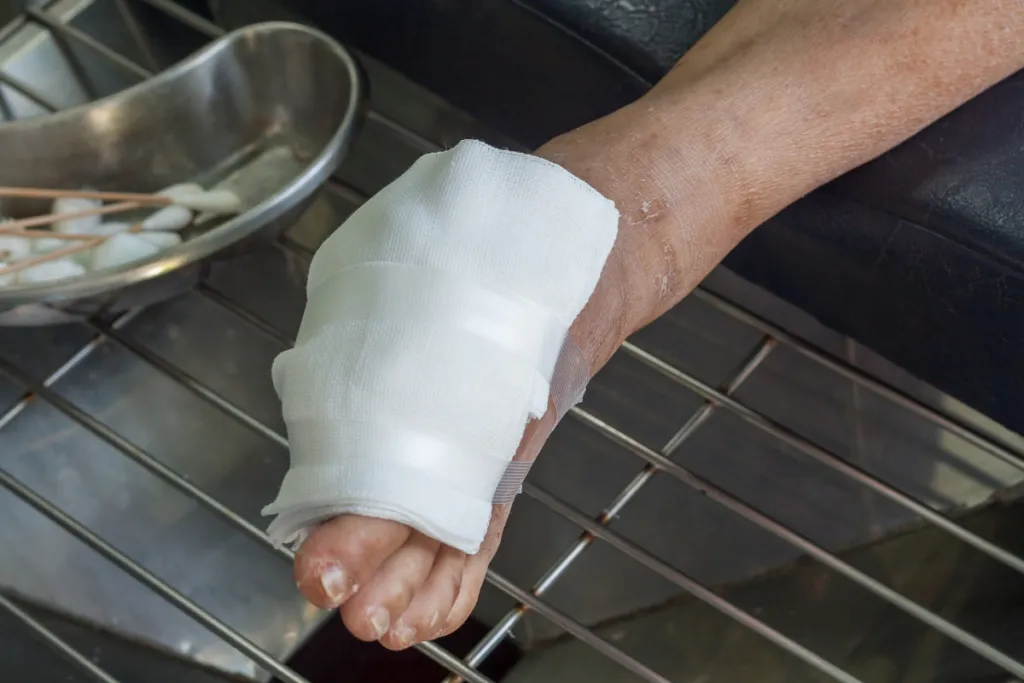
- Apply an antibiotic ointment and cover it with a sterile bandage.
- Avoid applying excessive pressure on the wound.
- Contact your healthcare provider immediately for assessment.
Delaying treatment can lead to severe infections. Find out about wound healing solutions.
4. Are there specific shoes recommended for diabetic foot care?
Yes, diabetic-friendly shoes should:
- Have a wide toe box to prevent friction and pressure sores.
- Offer cushioning and support to distribute weight evenly.
- Be made of breathable material to reduce moisture buildup.
You may also benefit from orthotic inserts. A podiatrist can recommend suitable footwear to protect your feet from injuries.
5. Can diet impact foot health in diabetes?
Absolutely! A healthy diet plays a crucial role in foot care by:
- Regulating blood sugar levels to prevent nerve and vascular damage.
- Providing essential nutrients like vitamin C and zinc for wound healing.
- Reducing inflammation that can worsen foot conditions.
Incorporating foods rich in omega-3s, fiber, and antioxidants can promote circulation and overall foot health.
Living with diabetes requires meticulous attention to foot health. High blood sugar levels can lead to nerve damage and poor circulation, increasing the risk of foot ulcers and infections. Implementing effective diabetic foot care strategies is essential to prevent these complications.
Understanding the Importance of Diabetic Foot Care
Diabetes affects millions of people worldwide and can lead to several complications, including issues with foot health. One of the most significant concerns for individuals with diabetes is the risk of peripheral neuropathy—nerve damage that reduces sensation in the feet. This can make it difficult to detect minor cuts, blisters, or injuries, which, if left untreated, can develop into serious ulcers or infections. Additionally, poor blood circulation associated with diabetes impairs the body’s ability to heal wounds, further increasing the risk of severe complications, including amputation.
Proper diabetic foot care is essential to prevent complications and maintain overall foot health. By adopting a proactive approach, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce their risk of foot-related issues. Below are some essential foot care tips to help ensure healthy feet.
Essential Diabetic Foot Care Tips
1. Daily Foot Inspections
Because diabetes can cause reduced sensation in the feet, regular self-examinations are critical. Early detection of problems can prevent complications such as ulcers or infections.
- Check your feet daily for cuts, blisters, redness, swelling, or sores.
- Use a mirror to inspect hard-to-see areas, or ask a family member for help if necessary.
- Look for changes in skin color, temperature, or signs of infection.
2. Maintain Foot Hygiene
Good hygiene can help prevent infections and other complications.
- Wash your feet daily using lukewarm water and mild soap.
- Dry your feet thoroughly, especially between the toes, as excess moisture can lead to fungal infections.
- Apply a moisturizer to keep your skin from becoming dry and cracked, but avoid applying lotion between the toes to reduce the risk of fungal growth.
3. Proper Nail Care
Untrimmed or improperly cut nails can lead to painful conditions such as ingrown toenails or infections.
- Trim your toenails straight across rather than rounding the edges to prevent ingrown nails.
- Use a nail file to smooth sharp edges.
- If you have difficulty cutting your nails, seek professional podiatric care.
4. Choose Appropriate Footwear
Wearing the right shoes can protect your feet from injury and provide necessary support.
- Select shoes that fit well, offer ample cushioning, and provide arch support.
- Avoid shoes that are too tight or too loose, as they can cause blisters and pressure sores.
- Always wear socks and shoes, even indoors, to prevent accidental injuries.
- Consider diabetic-friendly shoes that reduce pressure points and promote circulation.
5. Regular Physical Activity
Exercise plays a vital role in improving circulation and overall foot health.
- Engage in low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, or yoga to stimulate blood flow.
- Always wear appropriate footwear during physical activities to prevent injuries.
- Consult with your doctor before starting any new exercise routine.
6. Regular Medical Check-ups
Routine visits to a healthcare professional can help detect and address potential foot problems early.
- Schedule annual foot exams with a podiatrist or doctor.
- Seek immediate medical attention if you notice signs of infection, slow-healing wounds, or significant changes in foot health.
- If you have poor circulation or a history of foot ulcers, your doctor may recommend specialized diabetic foot care treatments.
The Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Even minor foot injuries can quickly escalate into serious complications for individuals with diabetes. Diabetic foot ulcers can lead to severe infections and, in extreme cases, may require amputation. However, early intervention and proper foot care can significantly reduce these risks.
By following the recommended foot care practices outlined above and seeking regular medical attention, individuals with diabetes can maintain healthy feet and an active lifestyle.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the following, consult a healthcare professional immediately:
- Persistent pain, numbness, or tingling in the feet.
- Non-healing wounds, ulcers, or open sores.
- Signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or pus.
- Changes in skin color or temperature.
- Cracks or bleeding between the toes.
Common Questions About Diabetic Foot Care
- Why are people with diabetes at higher risk for foot ulcers?
Diabetes can lead to nerve damage (neuropathy) and poor blood circulation, reducing the ability to feel injuries and heal wounds effectively. This combination increases the risk of developing foot ulcers. - How can I prevent diabetic foot ulcers?
Preventive measures include maintaining proper foot hygiene, wearing appropriate footwear, controlling blood sugar levels, and conducting daily foot inspections. Regular medical check-ups are also crucial. - What should I do if I notice a wound on my foot?
Clean the wound with mild soap and water, apply an antibiotic ointment, and cover it with a sterile bandage. Avoid putting pressure on the affected area and consult a healthcare professional promptly. - Are there specific shoes recommended for diabetic foot care?
Yes, shoes designed for diabetic individuals offer extra depth, cushioning, and support to reduce pressure points and prevent injuries. It’s advisable to consult a podiatrist for personalized recommendations. - Can diet impact foot health in diabetes?
Absolutely. A balanced diet helps regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of nerve damage and poor circulation, which are factors that can lead to foot ulcers.
How to Care for Your Feet with Diabetes | Ulcer Prevention Tips
Diabetes is a condition that affects multiple organs in the body, and one of the most vulnerable areas is the feet. High blood sugar levels can lead to nerve damage (neuropathy) and poor circulation, increasing the risk of foot ulcers, infections, and even amputation. Proper foot care is essential for individuals with diabetes to maintain overall health and mobility.
In this guide, we’ll explore the best foot care practices, prevention strategies, and expert recommendations for keeping your feet healthy when living with diabetes.
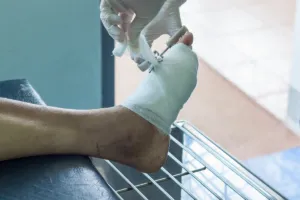
Why Is Foot Care Important for Diabetics?
People with diabetes are more prone to foot problems due to:
- Neuropathy (Nerve Damage): Reduces sensation, making it difficult to detect injuries.
- Poor Circulation: Slows down the healing process of wounds and cuts.
- Increased Risk of Infection: Even minor cuts or blisters can lead to serious infections.
- Higher Risk of Ulcers: Pressure points and injuries can develop into non-healing ulcers.
- Structural Changes: Diabetes can cause changes in foot shape, increasing the likelihood of pressure sores.
Proper foot care minimizes these risks, ensuring better mobility and quality of life.
Daily Foot Care Routine for Diabetics
A simple, consistent foot care routine can prevent complications and keep your feet healthy. Follow these essential steps:
1. Wash Your Feet Daily
- Use lukewarm water (not hot) and mild soap.
- Avoid soaking your feet for extended periods as it can lead to dryness.
- Dry your feet thoroughly, especially between the toes, to prevent fungal infections.
2. Moisturize to Prevent Dry Skin
- Apply a mild, unscented lotion to keep skin hydrated.
- Avoid applying lotion between the toes to prevent excessive moisture buildup, which can lead to infections.
3. Inspect Your Feet Daily
- Check for cuts, blisters, redness, swelling, or signs of infection.
- Use a mirror if you have difficulty seeing the bottom of your feet.
- If you notice any abnormalities, consult a podiatrist or wound care specialist.
4. Trim Toenails Properly
- Cut toenails straight across to prevent ingrown toenails.
- Avoid cutting too short or rounding the edges excessively.
- If you have difficulty trimming your nails, seek professional care.
5. Wear Proper Footwear
- Choose well-fitting, comfortable shoes with good arch support.
- Avoid tight or high-heeled shoes that can cause pressure points.
- Wear diabetic socks that wick away moisture and reduce friction.
6. Avoid Walking Barefoot
- Always wear shoes or slippers to prevent cuts and injuries.
- Inspect your shoes for foreign objects before wearing them.
7. Keep Blood Sugar Under Control
- Managing blood glucose levels helps prevent neuropathy and circulatory issues.
- Follow a balanced diet, stay active, and take prescribed medications.
8. Schedule Regular Foot Checkups
- Visit a podiatrist at least once a year for a comprehensive foot exam.
- Early detection of foot issues can prevent severe complications.
Signs of Diabetic Foot Problems
If you experience any of the following symptoms, seek medical attention immediately:
- Persistent pain or numbness in the feet
- Sores, blisters, or ulcers that do not heal
- Swelling or redness around a wound
- Foul-smelling discharge from an open sore
- Blackened skin (a sign of tissue death due to poor circulation)
Ignoring these warning signs can lead to severe infections and even amputation. Prompt wound care is critical for diabetic foot health.
Preventing Foot Ulcers and Complications
Diabetic foot ulcers are a leading cause of lower limb amputations, but they are largely preventable. Follow these key prevention strategies:
1. Protect Your Feet from Injuries
- Avoid walking barefoot, even indoors.
- Wear properly fitted shoes with soft insoles.
- Use cushioned socks to minimize friction.
2. Control Your Diabetes
- Maintain healthy blood sugar levels to promote healing.
- Monitor your HbA1c levels and follow your doctor’s recommendations.
3. Enhance Circulation
- Engage in gentle exercises like walking or swimming.
- Elevate your feet when sitting for long periods.
- Avoid smoking, as it restricts blood flow to the extremities.
4. Manage Calluses and Corns Carefully
- Do not attempt to remove calluses or corns yourself.
- Use a pumice stone gently after bathing to smooth rough areas.
- Seek professional care if you notice thickened skin or pressure points.
When to See a Specialist
If you have diabetes, regular foot exams are essential for preventing complications. See a wound care specialist or podiatrist if you notice:
- Persistent wounds or ulcers that don’t heal
- Increased pain, redness, or warmth in the feet
- Any signs of infection, such as pus or foul odor
- Changes in foot shape or skin color
Expert Diabetic Foot Care at OWC Center
At Optimum Wound Care Center (OWC Center), we specialize in diabetic foot care, wound management, and ulcer prevention. Our team provides:
- Comprehensive foot assessments
- Advanced wound care treatments
- Personalized prevention plans
- Education on diabetes management
If you or a loved one needs specialized diabetic foot care, contact OWC Center today to schedule an appointment.
Key Takeaways
- Daily Foot Inspections Prevent Complications
Checking your feet every day helps catch minor cuts, blisters, or signs of irritation before they worsen. Since diabetes can reduce sensation in your feet, injuries may go unnoticed without regular inspections. Early detection is crucial in preventing infections and ulcers. Learn more about diabetic foot care. - Proper Foot Hygiene Reduces Infection Risks
Washing your feet daily with mild soap and lukewarm water, followed by thorough drying, helps prevent bacterial growth and infections. Moisturizing your feet—except between the toes—keeps the skin healthy and less prone to cracks or wounds. - Choosing the Right Footwear Matters
Wearing well-fitted, cushioned shoes with a wide toe box reduces pressure points and lowers the risk of foot injuries. Avoid walking barefoot to prevent cuts or wounds that could turn into serious ulcers. Specialized diabetic footwear provides extra protection. Find expert guidance on diabetic wound care. - Blood Sugar Control Supports Wound Healing
High blood sugar levels can damage nerves and blood vessels, slowing the body’s ability to heal wounds. Maintaining stable glucose levels through a healthy diet and proper diabetes management significantly reduces the risk of foot ulcers and infections. - Regular Check-ups Ensure Early Intervention
Seeing a foot specialist regularly allows for early detection of issues before they escalate. Healthcare professionals can provide specialized treatments, recommend orthotics, and offer preventive care tailored to your needs. Schedule a consultation with our wound care specialists.