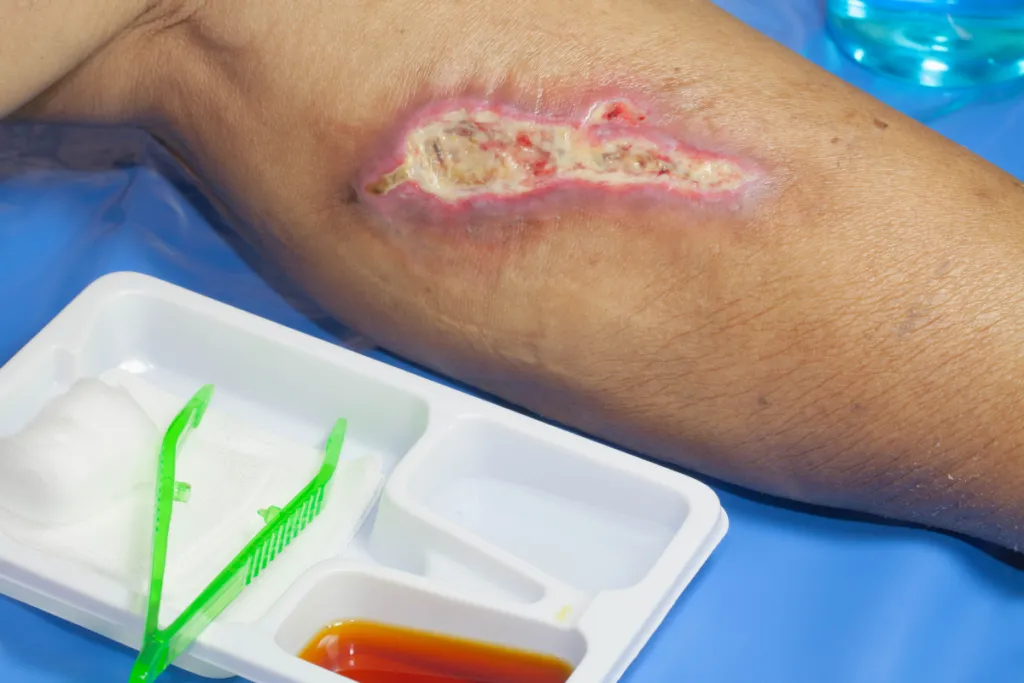
How to Prevent Wound Infections and Promote Healing
Cleanliness is key. Wash your hands. Use soap and water. Before touching the wound. Every time. Clean the wound gently. Avoid harsh chemicals. Apply an antibiotic ointment. Cover with a sterile bandage. Change dressings daily. Or as advised by your doctor. Avoid picking or scratching. Watch for signs of infection. Redness. Swelling. Warmth. Pus. If you notice any of these, seek medical help.
Recognizing Early Signs of Wound Infection
Early detection matters. Look for increased redness. Swelling around the wound. Pain that worsens. Warmth in the area. Pus or yellowish discharge. A foul smell. Fever or chills. These signs need attention. Don’t ignore them.
Proper Nutrition: Fueling Your Body for Healing
Your body needs fuel to heal. Protein helps tissue repair. Vitamin C boosts collagen production. Zinc aids cell repair. Iron supports oxygen transport. Stay hydrated. Eat a balanced diet. It makes a difference.
When to Consult a Doctor
While minor wounds often heal on their own, some require medical attention. Seek help if the wound is deep, bleeding doesn’t stop, or signs of infection appear. Consult a doctor if you have a fever, the wound isn’t healing after a few days, or you have a chronic condition like diabetes. Don’t wait—timely care is essential for your health.
Best Practices for Wound Healing and Infection Prevention
Follow your doctor’s instructions. Keep the wound covered. Stay active to improve blood flow. Manage underlying conditions. Avoid smoking and alcohol. Attend follow-up appointments. Take care of yourself.
Understanding Wound Infections
Wound infections occur when bacteria enter a break in the skin, leading to inflammation and delayed healing. Common signs include redness, swelling, warmth, pain, and discharge. In severe cases, infections can spread, causing systemic issues. Understanding the causes and symptoms is vital for effective prevention and treatment.
Wounds, whether minor cuts, surgical incisions, or chronic ulcers, are vulnerable to infection if not properly cared for. Preventing wound infections is crucial for faster healing and reducing complications. Following essential wound care steps can help keep infections at bay and promote optimal recovery.
Why Is Wound Infection Prevention Important?
A wound infection occurs when harmful bacteria enter the skin, leading to inflammation, delayed healing, and potential complications such as abscess formation or even systemic infections like sepsis. Proper wound care minimizes these risks, speeds up the healing process, and reduces the likelihood of scarring.
Essential Steps to Prevent Wound Infections

1. Maintain Hand Hygiene
Clean hands are the first line of defense against wound infections. Before touching a wound, always:
- Wash your hands with soap and warm water for at least 20 seconds.
- Dry hands with a clean towel or use an air dryer.
- Use alcohol-based hand sanitizer if soap and water are unavailable.
2. Clean the Wound Gently
Immediately after an injury, proper wound cleaning is vital:
- Rinse the wound under cool, running water to remove dirt and debris.
- Use a mild soap around the wound (avoid direct application inside deep wounds).
- Pat the area dry with a sterile gauze pad or a clean towel.
- Avoid using hydrogen peroxide or iodine, as they can damage healthy tissues.
3. Apply an Antibiotic Ointment
To prevent bacterial growth and aid healing:
- Apply a thin layer of antibiotic ointment such as bacitracin or Neosporin.
- Do not use excessive amounts; a light application is enough to protect the wound.
- If you have sensitive skin, consult your doctor for alternatives.
4. Cover the Wound with a Sterile Bandage
A clean bandage protects the wound from contaminants:
- Use a sterile, non-stick dressing to cover the wound.
- Secure with medical tape or adhesive strips if necessary.
- Ensure the bandage is changed daily or as advised by your healthcare provider.
5. Change Dressings Regularly
Proper dressing changes help maintain a clean environment:
- Always wash your hands before and after handling the wound.
- Replace the bandage if it becomes wet, dirty, or loose.
- If using specialized dressings for chronic wounds, follow medical guidance on frequency.
6. Avoid Touching, Picking, or Scratching
Touching the wound can introduce bacteria and delay healing:
- Refrain from picking at scabs or scratching around the wound.
- If itching occurs, apply a light moisturizer or consult your doctor.
- Keep fingernails short and clean to prevent accidental contamination.
7. Watch for Signs of Infection
Even with proper care, wounds can still become infected. Look out for:
- Redness that spreads beyond the wound edges.
- Swelling that doesn’t subside within a few days.
- Increased warmth around the affected area.
- Pus or drainage with an unusual color or foul odor.
- Pain that worsens instead of improving.
- Fever or chills, which may indicate a serious infection.
If you notice any of these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention to prevent complications
Recognizing Early Signs of Wound Infection
Early detection of an infection can prevent complications. Be alert for:
- Increased Redness and Swelling: Expanding redness or swelling around the wound.
- Pain or Tenderness: Pain that intensifies instead of diminishing over time.
- Warmth: The area around the wound feels warmer than the surrounding skin.
- Discharge: Presence of pus or yellowish fluid.
- Odor: Unpleasant smell emanating from the wound.
- Systemic Symptoms: Fever or chills, indicating a possible spread of infection.
Prompt medical attention is crucial if these symptoms occur.
Proper Nutrition: Fueling Your Body for Healing
Nutrition plays a vital role in wound healing:
- Protein: Essential for tissue repair. Include lean meats, eggs, and beans in your diet.
- Vitamin C: Aids collagen production and immune function. Citrus fruits and bell peppers are good sources.
- Zinc: Supports cell repair and immune defense. Found in nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
- Iron: Necessary for oxygen transport to tissues. Incorporate spinach, red meat, and lentils.
- Hydration: Drinking enough water keeps tissues hydrated, improves circulation, and aids in nutrient delivery for faster healing.
A balanced diet enhances healing and reduces infection risks.
Seek medical attention if:
- The wound is deep, large, or bleeding doesn’t stop.
- Signs of infection are present.
- You develop a fever or feel unwell.
- The wound isn’t healing after a few days.
- You have a chronic condition affecting healing, like diabetes.
Timely consultation prevents severe complications.
Best Practices for Wound Healing and Infection Prevention
To promote healing and prevent infections:
- Follow Medical Advice: Adhere to wound care instructions from healthcare providers.
- Keep the Wound Covered: Protect the wound until it fully heals.
- Maintain Physical Activity: Engage in activities, as advised, to improve blood circulation.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: Control chronic diseases that may impede healing.
Taking proactive steps in wound care can significantly reduce the risk of infection and promote faster healing. Simple yet effective measures—like keeping wounds clean, applying protective dressings, and monitoring for signs of infection—make a profound difference. Proper hand hygiene, good nutrition, and adherence to medical guidance all play a role in ensuring optimal recovery.
Recognizing early warning signs, such as redness, swelling, or unusual discharge, allows for timely intervention, preventing complications. Likewise, maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports the body’s natural healing process. For those with underlying health conditions or slow-healing wounds, seeking medical advice is crucial.
Ultimately, wound care is not just about healing an injury—it’s about fostering overall well-being. A mindful approach to prevention, treatment, and lifestyle habits ensures that wounds heal efficiently and safely, reducing the risk of long-term complications.
Key Takeaways
- Proper Wound Care Prevents Infections
Keeping wounds clean and covered is the first step in preventing infections. Washing hands before touching a wound, using mild soap and water, and applying antibiotic ointment help reduce bacterial risks. Always follow wound care best practices to promote faster healing and minimize complications. Learn more about wound care best practices here. - Early Infection Detection is Crucial
Recognizing early signs of infection—such as redness, swelling, warmth, pain, and discharge—can prevent severe complications. If symptoms worsen or a fever develops, seeking medical attention promptly is essential. Explore advanced infection management at OWCCenter. - Nutrition Plays a Vital Role in Healing
A well-balanced diet rich in protein, vitamin C, zinc, and iron strengthens the immune system and supports wound recovery. Proper hydration also promotes tissue repair and circulation, helping to reduce the risk of infections. Discover how nutrition supports wound healing. - Some Wounds Require Medical Attention
Not all wounds heal on their own. Deep wounds, slow-healing injuries, and infections require professional care—especially for individuals with diabetes or other chronic conditions. Ignoring an infected wound can lead to severe complications like cellulitis or sepsis. Find expert wound care services in Louisville. - A Proactive Approach Ensures Better Healing
Following medical advice, changing dressings as directed, managing underlying health conditions, and avoiding smoking and alcohol all contribute to optimal healing. Routine check-ups with a wound care specialist can further prevent complications. Schedule a consultation with a wound care expert.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wound Infections
1. How Can I Prevent a Wound Infection at Home?
Preventing wound infections at home is possible with proper wound care and hygiene. Here’s how you can keep wounds clean and lower infection risks:
- Wash your hands before and after touching the wound.
- Clean the wound gently with mild soap and water—avoid harsh chemicals like hydrogen peroxide.
- Apply an antibiotic ointment to reduce the risk of bacterial growth.
- Use sterile bandages to protect the wound from dirt and bacteria.
- Change dressings regularly, at least once a day or as instructed by your healthcare provider.
- Avoid picking or scratching at the wound, as it can introduce bacteria.
- Monitor for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, warmth, or pus.
If you notice any signs of infection, consult a wound care specialist in Louisville immediately.
2. What Are the Early Signs of a Wound Infection?
Recognizing the early signs of an infection can prevent complications. Here’s what to watch for:
- Increased redness and swelling around the wound
- Pain or tenderness that worsens instead of improving
- Warmth around the affected area
- Pus or yellowish discharge from the wound
- A foul odor from the wound site
- Fever or chills, which may indicate a systemic infection
Early intervention is crucial. If you experience these symptoms, seek advanced wound care to prevent serious complications.
3. How Does Proper Nutrition Help Prevent Wound Infections?
Nutrition plays a vital role in wound healing and infection prevention. Your body needs essential nutrients to support tissue repair and immune function:
- Protein: Supports tissue regeneration (e.g., lean meats, eggs, beans)
- Vitamin C: Boosts collagen production and immune response (e.g., citrus fruits, bell peppers)
- Zinc: Helps with cell repair and immune defense (e.g., nuts, seeds, whole grains)
- Iron: Supports oxygen transport to tissues (e.g., spinach, red meat, lentils)
- Hydration: Keeps tissues healthy and promotes circulation
A well-balanced diet can improve healing time and reduce infection risks. Consider working with a wound care provider to optimize your nutrition.
4. When Should I See a Doctor for a Wound Infection?
While many minor wounds heal on their own, some require medical attention. Seek professional help if:
- The wound is deep, large, or does not stop bleeding
- You see signs of infection (swelling, redness, pus, or warmth)
- You develop a fever or feel unwell
- The wound is not healing properly after a few days
- You have a chronic condition (such as diabetes) that affects wound healing
Ignoring an infected wound can lead to severe complications like cellulitis or sepsis. If you’re in Louisville, KY, visit OWC Center for specialized treatment.
5. What Are the Best Practices for Wound Healing and Infection Prevention?
To ensure optimal healing and infection prevention, follow these expert-recommended practices:
- Follow your doctor’s wound care instructions carefully.
- Keep the wound covered and protected until it fully heals.
- Stay active (as advised by your doctor) to improve blood circulation.
- Manage underlying conditions like diabetes, which can slow healing.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol, as they impair healing and immune response.
- Attend follow-up appointments to track your healing progress.
For professional wound care and infection management, consider Optimum Wound Care Center.